As businesses and public sector organizations increasingly adopt AI technologies to drive innovation, efficiency, and growth, they face many challenges in ensuring these systems’ trustworthiness and reliability. Building trust in an AI-driven future requires a comprehensive approach beyond the mere fascination with technological advancements, from the veracity of data sources to the prevention of identity theft and fraud.
The ecosystem of trust in AI is complex and multifaceted, involving a delicate balance between the benefits of automation and the need for robust security measures. It is not enough to simply marvel at the potential of AI; organizations must actively work towards establishing a framework that instills confidence among stakeholders and the public at large.
The European Commission has also examined the matter, defining a framework with the AI Act. Indeed, as part of its Digital Agenda, the EU wants to regulate artificial intelligence (AI) to ensure better conditions for developing and using this innovative technology. AI can bring many benefits, such as better healthcare, safer and cleaner transport, more efficient manufacturing, and cheaper, more sustainable energy.
This blog post explores the key factors contributing to building trust in an AI-driven future, focusing on the critical role of digital trust authentication, combating identity theft and fraud, ensuring the veracity of sources, and fostering a collaborative and transparent AI ecosystem.
As we navigate the uncharted waters of an AI-powered world, businesses and public sector players must understand and address the concerns surrounding trust and security. By examining the challenges and best practices in digital trust authentication, this post aims to provide valuable insights and guidance for organizations seeking to harness the power of AI while maintaining the highest standards of integrity and reliability. Join us as we delve into the factors that can give confidence in an AI future and explore how the ecosystem can organize itself to respond to the growing demand for trust and assurance.
The Role of Digital Trust Authentication in an AI-Driven Landscape
In an AI-driven future, digital trust authentication is critical in ensuring secure and reliable interactions between humans and machines.
At its core, digital trust authentication refers to verifying the identity and legitimacy of users, devices, and data sources in digital environments. The need for robust authentication mechanisms becomes paramount as AI systems become increasingly autonomous and make decisions that impact individuals and organizations.
The significance of digital trust authentication in AI-powered systems cannot be overstated.
Consider the following key points:
- Preventing unauthorized access: By implementing robust authentication protocols, organizations can safeguard their AI systems, protect sensitive data, and prevent malicious actors from manipulating or corrupting the algorithms.
- Ensuring data integrity: Digital trust authentication plays a vital role in verifying the authenticity and integrity of data sources used to train and operate AI models. This helps maintain the accuracy and reliability of AI-driven insights and decisions.
- Enhancing user confidence: When users interact with AI-powered applications, such as virtual assistants or personalized recommendation engines, they need assurance that their personal information is secure and that the system is trustworthy. Digital trust authentication provides this assurance, fostering user confidence and adoption.
As AI technologies advance, they can be leveraged to enhance authentication processes through techniques like biometric recognition, behavioral analysis, and anomaly detection. Conversely, robust digital trust authentication frameworks are essential to ensure AI systems’ responsible and ethical deployment, mitigating risks associated with data privacy, bias, and security vulnerabilities.
To effectively integrate digital trust authentication into AI systems, organizations should consider the following best practices:
- Implement multi-factor authentication: Combining multiple authentication factors, such as passwords, biometrics, and hardware tokens, adds an extra layer of security to AI systems, reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
- Update and patch authentication mechanisms regularly: As threats evolve, it is crucial to keep authentication systems up to date with the latest security patches and protocols to maintain their effectiveness.
- Conduct thorough testing and auditing: Organizations should regularly test and audit their digital trust authentication mechanisms to identify and address any vulnerabilities or weaknesses in the system.
- Foster a culture of security awareness: Educating employees and users about the importance of digital trust authentication and best practices for secure access can help create a strong foundation for trust in AI-driven environments.
Businesses and public sector organizations can lay the groundwork for a secure and reliable AI ecosystem by prioritizing digital trust authentication. In the next section, we will explore the challenges of combating identity theft and fraud in the age of AI and discuss strategies for mitigating these risks.
Combating Identity Theft and Fraud in the Age of AI
As AI technologies become more sophisticated and integrated into various aspects of our lives, identity theft and fraud risks have also evolved. Fraudsters and cybercriminals are leveraging AI-powered tools to carry out more complex and harder-to-detect attacks, posing significant challenges for businesses and public sector organizations. To combat these threats effectively, it is essential to understand the common types of identity theft and fraud in AI systems and implement robust authentication measures.
Some of the most prevalent forms of identity theft and fraud in AI-driven environments include:
- Deepfake fraud: Criminals use AI algorithms to create highly realistic fake videos or audio recordings of individuals, which they can use for social engineering attacks or to manipulate public opinion. As a chart based on the most recent annual report of identity verification provider Sumsub shows, deepfake-related identity fraud cases have skyrocketed between 2022 and 2023 in many countries around the world.
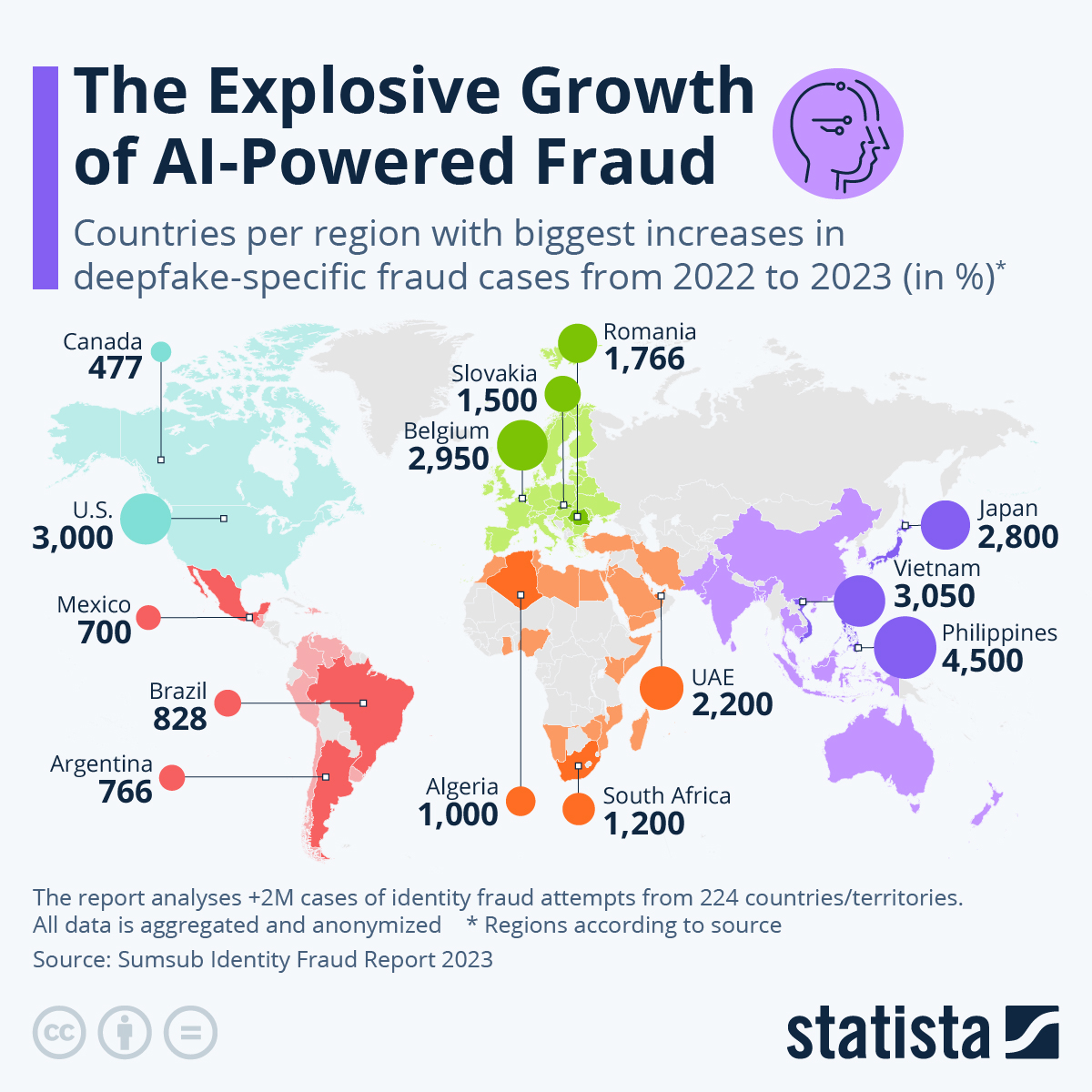
- Synthetic identity fraud: By combining accurate and fake personal information, fraudsters can create entirely new, synthetic identities that are difficult to detect using traditional authentication methods.
- AI-powered phishing: Attackers employ AI algorithms to analyze social media profiles and craft highly personalized phishing emails, increasing the likelihood of successful attacks.
Organizations must adopt a multi-layered approach to authentication and security to prevent and detect these fraudulent activities.
Some best practices include:
- Implementing AI-driven anomaly detection: Organizations can identify potential fraud attempts in real-time by leveraging machine learning algorithms to analyze user behavior and detect unusual patterns.
- Strengthening identity verification processes: Combining traditional authentication methods with advanced techniques like biometric recognition and document verification can help ensure the legitimacy of user identities.
- Promoting fraud awareness and education: Regularly training employees and users on the latest fraud tactics and best practices for maintaining security can help create a more resilient ecosystem.
- Collaborating with industry partners: Sharing threat intelligence and best practices among organizations can help identify emerging fraud patterns and develop collective mitigation strategies.
In addition to these measures, organizations must also prioritize the development of ethical and transparent AI systems. Organizations can build trust with their stakeholders and reduce the risk of unintended consequences by ensuring that AI algorithms are free from bias and that decision-making processes are explainable.
As we continue to navigate the challenges of identity theft and fraud in an AI-driven world, businesses and public sector players must remain vigilant and proactive in their approach to security. By adopting robust authentication measures and fostering a culture of trust and transparency, organizations can harness AI’s power while safeguarding their stakeholders’ interests.
Ensuring the Veracity of Sources and Information in AI Systems
The effectiveness and reliability of AI systems heavily depend on the quality and integrity of the data they process. As organizations increasingly rely on AI to make critical decisions and drive business outcomes, ensuring the veracity of sources and information becomes a top priority. Inaccurate, biased, or manipulated data can lead to flawed AI models, erroneous conclusions, and a loss of trust among stakeholders.
One of the primary challenges in maintaining data veracity in AI systems is the sheer volume and variety of data sources;
With the proliferation of big data and the Internet of Things (IoT), organizations must contend with a constant influx of structured and unstructured data from multiple sources, including sensors, social media, and third-party providers. Validating the authenticity and accuracy of this data can be a daunting task.
To address this challenge, organizations can implement several techniques and best practices for data validation and governance:
- Data lineage tracking: By documenting the origin, movement, and transformation of data throughout its lifecycle, organizations can maintain a clear audit trail and quickly identify any issues or anomalies.
- Data quality assessments: Regularly conducting data quality assessments can help identify errors, inconsistencies, and gaps in the data, allowing organizations to take corrective action before the data is used in AI models.
- Blockchain-based data verification: Leveraging blockchain technology can provide an immutable and transparent record of data transactions, ensuring the integrity and authenticity of data sources.
- Collaborative data governance: Establishing cross-functional data governance teams that include IT, business, and compliance representatives can help ensure that data policies and standards are consistently applied across the organization.
In addition to these technical measures, organizations must foster a data literacy and accountability culture. Organizations can create a more resilient and trustworthy data ecosystem by educating employees about the importance of data quality and providing them with the tools and resources to identify and report data issues.
Moreover, organizations should be transparent about their data sourcing and processing practices. By clearly communicating how data is collected, validated, and used in AI systems, organizations can build trust with their stakeholders and demonstrate their commitment to responsible AI development.
Ensuring the veracity of sources and information will remain a critical challenge as the AI landscape evolves. By adopting robust data governance practices, investing in data validation technologies, and promoting a culture of data literacy and transparency, organizations can lay the foundation for a more trustworthy and reliable AI ecosystem.
Building a Trustworthy AI Ecosystem
Creating a trustworthy AI ecosystem requires a collaborative effort from all stakeholders, including businesses, public sector organizations, technology providers, and regulatory bodies. By establishing industry standards, best practices, and governance frameworks, these stakeholders can foster an environment that promotes responsible AI development and deployment.
One key aspect of building a trustworthy AI ecosystem is establishing clear and consistent industry standards. These standards should cover various aspects of AI development, including data privacy, security, ethics, and transparency. By adhering to these standards, organizations can ensure that their AI systems are developed and deployed in a manner that prioritizes the interests of users and society as a whole.
Another critical component of a trustworthy AI ecosystem is collaboration among stakeholders. By sharing knowledge, best practices, and resources, organizations can accelerate the development of secure and reliable AI solutions. This collaboration can take many forms, such as:
- Industry consortia: Bringing together organizations from different sectors to address common challenges and develop shared solutions.
- Public-private partnerships: Fostering collaboration between businesses and government agencies to ensure that AI development aligns with public policy goals and societal values.
- Open-source initiatives: Encouraging the sharing of AI tools, frameworks, and datasets to promote transparency and innovation.
Transparency is also a crucial factor in building trust in AI systems. Organizations must be open and transparent about how their AI systems are developed, trained, and deployed. This includes providing information about the data sources, algorithms employed, and decision-making processes. By being transparent, organizations can help stakeholders understand the capabilities and limitations of AI systems and foster a sense of accountability.
A trustworthy AI ecosystem requires ongoing monitoring and evaluation. Organizations must regularly assess the performance and impact of their AI systems to identify and address any unintended consequences or biases. This may involve conducting regular audits, seeking feedback from users and stakeholders, and implementing mechanisms for redress and accountability.
Building a trustworthy AI ecosystem is a complex and ongoing process that requires the commitment and collaboration of all stakeholders. By establishing clear standards, fostering collaboration, promoting transparency, and prioritizing explainable and accountable AI, organizations can create an environment that maximizes AI’s benefits while mitigating its risks.
Conclusion
In conclusion, building trust in an AI-driven future requires a multifaceted approach that addresses the various challenges and concerns surrounding AI development and deployment. From ensuring the veracity of data sources to combating identity theft and fraud, organizations must prioritize the development of secure, reliable, and transparent AI systems.
Digital trust authentication emerges as a critical component in this ecosystem, providing safeguards to protect user identities and prevent unauthorized access. By implementing robust authentication measures and regularly updating and testing these systems, organizations can create a strong foundation for trust in AI-powered environments.
Moreover, organizations can create a trustworthy AI ecosystem that benefits all by fostering collaboration among stakeholders, establishing clear industry standards, and promoting transparency and explainability in AI development. As we move into an increasingly AI-driven future, businesses and public sector players need to remain vigilant, proactive, and committed to building trust at every step.
By prioritizing trust and security in AI development, we can unlock the full potential of this transformative technology while ensuring that it serves the interests of individuals, organizations, and society as a whole.